Internship Report on Himalayan Bank Limited
CHAPTER ONE
INTRODUCTION
1.1 Background of Study
Bachelor in
Business Administration (BBA) program is run by Tribhuvan University from 2002
under the supervision of the Faculty of Management (FOM). It aims to provide
quality education through quality and professional courses. BBA is four years
international standard program consisting of eight semesters along with
internship program. Thus, BBA program is a blend of theoretical and practical
knowledge on the financial sector enabling the students in understanding
business environment and solving practical business problems. It also aims to
develop creative, socially responsible and skilled professionals who are able
to carry out the responsibility of middle level managerial positions in the
rapidly growing business sector in Nepal as well as abroad.
Theoretical
knowledge is not sufficient in this competitive and complex business world.
Thus, in the eight semester of BBA program, student is required
to work in financial institution for at-least eight weeks, where they can
experience real situations of work environment in the organization. It also
helps in understanding organizational environment and work culture. Internship
program enables in acquiring skills and techniques by experiencing practical work situations
directly applicable to develop career on financial sectors. It may also create
the opportunities for placements in the same host organization or other
organizations.
1.2 Objective of Report
After the
completion of internship program, it is required to prepare the report to be
acquainted with what the student have learnt in the host organization over the
internship period. It helps to share the experience of student along with
problem faced by them. The main objective of the study is to highlight the
activities carried out in Himalayan Bank Limited, Thamel Branch and to get the
practical exposure to the organization’s environment and gaining the practical
knowledge to deal with the real management problems through various managerial
skills. The specific objectives of this study are:
·
To
provide a brief synopsis on the present scenario of Nepalese banking sector.
·
To
enlighten the task performed in HBL under various departments.
·
To
comprehend the operational system of HBL.
·
To
give details of the product and services provided by the HBL.
·
To
build self-confidence and experience in the work environment.
1.3 Methodology
This
internship report is based on research methodology. It helped to analyze the
data in finding the cause and effect relationship to see how bank is
performing. Since, research is a scientific discipline; it needs much more
attention on the part of the researcher.
1.3.1 Organization Selection
Decision
about the organization selection for the internship program is very crucial
task due to existence of different financial institutions in the Nepalese
financial market. Internship from a reputed organization definitely enlarges
the prospects of gaining more practical knowledge and also enhances confidence
of every student. Since I did
specialization on Banking and Finance I selected to do internship in the
Banking institution to boost my knowledge. As commercial banks are 'A' class
financial institutions I chose them among other financial institutions. I
dropped the college recommendation letter and personal application with resume
in Himalayan Bank Ltd. since it is one of the reputed banking institutions with
great operations. Further, I did regular follow–up with the human resource
department of HBL. After screening my
resume by the Human Resource Department of HBL I was selected for internship placement.
1.3.2 Placement
As concern
to my placement in HBL, throughout my internship period I was placed in Thamel
branch. There I got an opportunity to work in different department such as
bills and remittance department, customer service department, trade finance,
customer relation department, credit management and administration department.
The task was assigned as per the requirement of the different department under
the supervision of respective department head. I was fortunate enough to gain
knowledge on various departments under proper supervision of department heads
and staffs during the internship period. I presented myself with full
confidence and well-disciplined in this institution and created mutual trust
among the staffs and got the opportunity to learn functioning of different
departments.
1.3.3 Duration of Internship
The duration
of internship period has been declared for minimum 8 weeks by FOM, Tribhuvan
University. During eighth semester, student should complete internship acquire
six credit hours. As per the requirement, the internship was carried out from
June 15, 2012 to August 13, 2012 in
HBL, Thamel branch from 10:00 am and to 5:00 pm
in different departments. In this period I was placed in various departments so
that I could develop knowledge about various activities performed in each
department making me able to achieve practical; disclosure to functioning
process.
Table 1.1 Duration of
Internship
|
Departments/
Weeks
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
6
|
7
|
8
|
|
Bills and Remittance
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Customer Service
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Letter of Credit
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Customer Relation
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Credit management and administration
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.3.4 Information Collection Methods
The primary
as well as secondary information has been used to prepare this report.
Ø
Primary Sources
a.
Observation
during internship in HBL
b.
Questionnaire
with employees and customers of HBL
c.
Files,
registers, computer data
Ø Secondary
Sources
a. Internet Surfing
b.
Reports
and Brochures
c.
Publications
and journals
1.4 Limitations of the Study
Every activity is chase by the
boundaries and limitations. So, the same tendency happens while preparing this
internship report. Some constraints faced during preparing this report are
listed below:
·
This study is mainly concentrated on
activities done during internship period.
·
Due to limited time, the study has been
conducted quickly.
·
Less interaction and guidance by the staffs
to the intern due to their own rush.
·
As internship period was during closing of
the fiscal year i.e. Ashad, bank's staffs have excess workload due to which
they cannot supervise the intern properly.
·
Because of rush, interns were confined to
routine job of the bank and was not able to acquire crucial information of the
bank.
·
Being a student, lack of technical knowledge
was another factor which limits the report.
·
This report is based on my individual
experience, ideas and skills achieved during the internship period rather than
theoretical knowledge.
·
The details of prescribed departments and its
transaction were not provided to intern due to confidentiality reasons and
policies of the bank.
CHAPTER TWO
INTRODUCTION OF THE INDUSTRY
2.1 Introduction of Bank
After commerce and the arts
had revived in Italy, the business of banking was resumed.
The word "bank" is commonly regarded as derived from the Italian word
'Banco', a bench - the Jews in Lombardy having benches in the market-place for
the exchange of money and
bills. And people around the world start to use different words for their
convenient like in French 'Banque', Latin 'Bancus', and German 'Bank'. At
ancient times, bank means moneylenders who sat in the bench for keeping,
lending and exchanging of money in the market place.
A bank is an
institution which deals in money receiving as deposits from customers, honoring
customers drawing against such deposits on demand, collecting cheques for
customers and lending or investing surplus deposits until they are requires for
repayment. It allows interest on the deposits made and charges
interest on the loans granted and further it creates credit and supports for
the formation of capital and hence it is regarded as manufacturer of money.
In simple, bank is an institution which deals with money and
credit. A bank is a financial institution that serves as a financial
intermediary, who bridges
gap between the savers of the fund and users of the funds. Nowadays, a bank has
broadened its scope by providing financial as well as non-financial services to
its customers. To give specific meaning of bank is very difficult task however
following are the few definitions given by different authors.
"Banking means the accepting for the purpose of lending or investment of
deposits of money from the public, repayable on demand or otherwise and
withdrawal by cheque draft order or otherwise." --Indian Banking
Company Act 1949
"Bank is an organization established
for the purpose of exchange money deposit lending money and participation in
transactions." --Commercial Bank Act of 2031
"Bank is a financial institution, which
provides financial services that may be in the form of accepting deposits,
advancing loan, providing necessary technical advices, dealing overt foreign
currencies, remitting funds, etc." –Nepal Rastra Bank Act 2002
From the
above definitions, we draw the conclusion that a bank is a financial
intermediary that accepts deposits and channels those deposits into lending
activities, either directly or through capital markets. It is the most
important financial institution dealing with money, receiving it as deposits
from customers, honoring customers drawing against such deposits on demand,
collecting cheques for customers and lending or investing surplus deposits
until they are required for repayment.
Thus, bank
receives demand deposits and time deposits, honors instruments drawn on them,
and pays interest on them, makes loans, and invests in securities, collects
cheques, drafts and certifies depositor's cheques and issues drafts and
cashier's cheques. The difference in interest rate on lending and deposit,
interest rate spread, is the major source of income for the bank. Interest on
lending is higher than the deposits.
2.2 History of Banking in Global Scenario
The history
of banking is nearly as old as civilization. In the Babylon, at the time of Hammurabi,
in the 18th century BC, there are records of loans made by the priests of the
temple. The concept of banking has arrived. When the word bank is used
it is meant for commercial bank. Before 1960 there was no such word as
“banking’. However, in the temple Babylon the practices of safeguarding and
saving flourished as early as 2000 B.C. Chanakya in his Arthashastra written in
about 300 B.C. mentioning about the existence of powerful guilds of merchant’s
bankers received deposits, advance loans and hundies. Merchants and goldsmith
were ancestors of bank.
The 'Bank of
Venice', established in1157 A.D. is supposed to be the ancient bank.
Originally, it was not a bank in real sense being simply on office for the
transfer of the public debt. Venice, after being possibly the first city to
found a bank for the keeping of money on safe deposit and the clearing of
cheques, is also a pioneer in the involvement of a bank with state financiers.
In 1617 the BancoGiro is established to solve problems encountered by the
earlier, which has got into trouble through the making of unsecured loans. Subsequently, 'Bank
of Barcelona' (1401) and 'Bank of Geneva' (1407) were established.
During the
18th century the Bank of England gradually undertakes many of the tasks now
associated with a central bank, The 'Bank of England', first English Bank, was
established in1964 A.D. It organizes the
sale of government bonds when funds need to be raised. It acts as a clearing
bank for government departments, facilitating and processing their daily
transactions.
History
apart, it was the “Merchant bank” that first evolved the system by trading in
commodities than money. They used to do their trading activities by remitting
the money from one place to another. The next stage in the growth of banking
was goldsmith. An honest goldsmith was also trusted with billions money and
ornaments by merchants in neighborhoods. He started charging for acting as
custodians of these valuables. As an evidence for receiving valuables he issued
a receipt, which in turn became like cheques as a mode of exchange. He started
advancing the coins on loan by charging interest. He started to keep some
reserve as a safeguard. In this way the goldsmith money lender became a banker
who started performing the two functions of modern banking that of accepting
deposits and advancing loans.
2.3 History of Banking in Nepal
Banking service is the oldest service industry in Nepal. It
has gone through various stages of evolution and development since the Vedic
times (2000 to 1400 B.C.). In the Nepalese chronicles, it was recorded that the
new era known as Nepal Sambat was introduced by Shankhadhar, a Sudra merchant
of Kantipur in 880 A.D.
The banking in the form of money leading can be traced back in
the reign of Gun Kam Dev towards the end of 8th century. According to the
historical evidence in 723 Gun Kam Dev, the king of Kathmandu had borrowed
money to rebuild and to rule Kathmandu.
In the 11th century, during Malla regime, there was an evidence
of professional money-lenders and bankers. It is further believed that
money-lending business, particularly for financing the foreign trade with
Tibet, became quite popular.
Another historical example as to the pre-modern banking
system is found when Rana Prime minister Randip Singh was administering Nepal
in 1880 A.D. During his regime one financial institution name by
"TejarathAdda" was establish to give loan facilities to the
governmental staff and to afford loan facilities to the public in general in
the term of 5% interest. The credit facilities of "TejarathAdda" were
also extended outside the valley during the Prime Minister ship of Chandra
Shumsher Rana. Although this institution did not accept any deposits, it had
played an important role in the development process of banking system in Nepal.
Modern banking business started in the country just before the Second World
War. In 1938 state financial institute which supply credit or loan against
security.
His Majesty
King Tribhuvan inaugurated first commercial bank i.e. Nepal Bank Limited on
Kartik 30, 1994 B.S. In the year 1994 B.S. as a semi government organization
with an authorized capital RS.10 million of which 51% share are owned by
government, this marked the beginning of an era of formal banking in Nepal.
Until then all monetary tractions were carried out by private dealers and
trading center.
The need to
regulate financial and monetary system increased enormously resulting in the
establishment of Nepal Rastra Bank in 2013 B.S. In order to cater the demand of
banking system, Rastriya Banijya Bank was established in 2022 B.S with 100%
government ownership.
Later some
development banks and financial institutions were established to provide medium
and long-term credit facilities to the industry and agriculture. In this contest, Nepal Industrial Development
Corporation was established in 2016 B.S. to provide the financial and
managerial assistance in the field of industry and to help private sector in the
field of industry. In order to provide service to the agriculture sector,
Agriculture Development Bank Ltd. was established in 2024 B.S.
The
government of Nepal adopted liberal economic policy to accelerate country's
growth and development. Foreign investment and participation of private sector
were encouraged. The government then enacted "Joint Venture Banking"
policy. Commercial Banks should operate under the Commercial Bank Act 2031,
Nepal Rastra Bank Act 2058 and Contract Act 2056. Nepal Arab Bank Ltd.
(currently known as NABIL) is the first bank established in joint investment in
Nepal in 2041 B.S. With the passage of time several other joint venture and
private bank has been established such as Indosuez bank Limited (Nepal
investment bank) in 2042 B.S., Nepal Grindlays Bank (Standard Chartered bank)
2043 B.S., Himalayan Bank Limited in 2049 B.S. and so on.
2.4 Present Scenario of Nepalese Financial System
Financial
system is the set of financial institutions, financial market, and financial
instruments along with regulations and laws. Financial system facilitates
resources transfer and mobilizes savings to the productive sectors thereby
contributing to the economic development.
Commercial
Banks are the heart of our financial system. A commercial
bank (or business
bank) is a type of financial
institution and intermediary.
It is a bank that provides transactional,
savings, and money market accounts and that accepts time
deposits. They hold the deposits of millions of persons,
governments and business units. They
make funds, available through their lending and investing activities to
borrowers, individual business firms and government. Therefore the task of
commercial banks in an under developed countries is almost self-evident. Their
purpose is to provide a collecting point for savings of a relatively small
average amount from a large number if individual source so long as to utilize
savings safely and profitably.
Hence,
commercial bank is the financial institution authorized to receive both time
and demand deposits, to make loans of various types, to engage in trust
services, to issue letters of credit, to accept and pay drafts, to rent safety
deposit boxes, and to engage in similar activities and ventures.
Financial
institutions are the organization that channelizes the savings of government,
businesses and individual into loans and investment. It consists of:
·
Depository Institutions
Depository
institutions are the banking institutions which collect amount through deposits
accounts and sold bulk amount through loan account. In Nepal, NRB has
classified depository institutions as follows:
Table 2.1 List of no.
of depository institutions
|
Class
|
Financial Institutions
|
No. of Institutions
|
|
A
B
C
D
|
Commercial Bank
Development Bank
Finance Companies
Micro Credit Development Banks
|
32
88
70
24
|
Source: www.nrb.org.np
·
Non-depository Institutions
Non-depository
institutions are an intermediary who does not accept the deposit directly from
the customers. They are insurance companies, investment banks, pension funds,
etc.
2.5 Functions
of Commercial Banks
The
functions of commercial banks are divided into two categories:
I.
Primary Functions
The primary functions of a commercial
bank include:
|
A.
Acceptance of Deposits
v Currents deposits (demand
deposits)
v Savings deposits
v Fixed deposits
v Recurring deposit
v Miscellaneous deposits (Home
construction deposit scheme, Sickness benefit scheme, Children plan, Old age
pension scheme, etc)
|
B. Granting
loans and advances
v Loans (Credit facility for more
than 1 year)
i.
Demand
loan
ii.
Term
loan
v Advances (Short-term financial
assistance)
i.
Cash
Credit
ii.
Bank
Overdraft
iii.
Discounting
of Bill
|
II.
Secondary functions including
agency functions.
·
Issuing
letter of credit, travelers' cheques, circular notes etc.
·
Undertaking
safe custody of valuables, important documents, and securities by providing
safe deposit vaults or lockers.
·
Providing
customers with facilities of foreign exchange.
·
Transferring
money from one place to another and from one branch to another branch of the
bank.
·
Standing
guarantee on behalf of its customers, for making payments for purchase of
goods, machinery, vehicles etc.
·
Collecting
and supplying business information.
·
Issuing
demand drafts and pay orders and,
·
Providing
reports on the credit worthiness of customers.
2.6 Agency and General Utility Services provided by
Modern Commercial Banks
Besides
these two main activities, commercial banks also render a number of ancillary
services. These services supplement the main activities of the banks. They are
essentially non-banking in nature and broadly fall under two categories:
I) Agency Services
Agency
services are those services which are rendered by commercial banks as agents of
their customers. They include:
Ø
Collection
and payment of cheques and bills on behalf of the customers;
Ø
Collection
of dividends, interest and rent, etc. on behalf of customers, if instructed by
them.
Ø
Purchase
and sale of shares and securities on behalf of customers
Ø
Payment
of rent, interest, insurance premium, etc. on behalf of customers, if
instructed.
II) General utility services
General
utility services are those services which are rendered by commercial banks not
only to the customers but also to the general public. These are available to
the public on payment of a fee or charge.
They
include:
Ø
Issuing
letters of credit and travelers' cheques.
Ø
Underwriting
of shares, debentures, etc.
Ø
Safe-keeping
of valuables in safe deposit locker.
Ø
Supplying
trade information and statistical data useful to customers.
Ø
Undertaking
foreign exchange business.
2.7 Commercial Banks in Nepal
The year 1994
B.S. marks the beginning of new era, in the history of modern banking in Nepal.
Thus, we see the establishment of its first commercial bank i.e. Nepal Bank
Ltd. In the year 1994 B.S. as a semi government organization with an authorized
capital RS.10 million of which 51% share are owned by government within few
years of its establishment it extended a number of branches.
As the
time passed “Rastriya Banijya Bank” was established in 1966 A.D. in order to
play a major role not only in domestic banking services but also in foreign
trade. As the country followed economic liberalization, there was massive
entrance of foreign banks in Nepal. Nepal Indosuez Bank was established as a
joint venture between Nepal and France in 1986 A.D. Similarly, Nepal Grind lays
bank (Standard Chartered bank) was established in 2043 B.S. and Himalayan Bank
Ltd. was also established in 2049 B.S. with joint venture with Habib Bank Ltd.,
Pakistan.
Till 2068 there are many commercial banks as
well as development banks that have been working smoothly in Nepal. The
licensed commercial banks according to the central bank of Nepal i.e. NRB are
32 and they are listed in annex 1.
CHAPTER
THREE
INTRODUCTION OF THE ORGANIZATION
3.1 An Overview of Himalayan Bank Limited
Himalayan Bank was established in 1993 in joint venture with Habib
Bank Limited of Pakistan. Despite the cut-throat competition in the Nepalese
Banking sector, Himalayan Bank has been able to maintain a lead in the primary
banking activities- Loans and Deposits. It
goes with a punch line “The Power to Lead”.
Legacy of Himalayan lives on in an institution that's known
throughout Nepal for its innovative approaches to merchandising and customer
service. Products such as Premium Savings Account, HBL Proprietary Card and
Millionaire Deposit Scheme besides services such as ATMs and Tele-banking were
first introduced by HBL. Other financial institutions in the country have been
following our lead by introducing similar products and services. Therefore, HBL
stand for the innovations that bring about in this country to help customers
besides modernizing the banking sector. With the highest deposit base and loan
portfolio amongst private sector banks and extending guarantees to
correspondent banks covering exposure of other local banks under the credit standing with foreign correspondent
banks, HBL believe it as lead the banking sector of Nepal. The last year rating
of HBL by Bankers’ Almanac as country’s number 1 Bank easily confirms our
claim. Other awards
and recognitions received by the bank in the past 6 years also ranks the bank
in high positions with awards like:
· Best
Presented Account Award- 2008 awarded by The Institute of Chartered Accountants
of Nepal.
· Number
1 bank of Nepal-2006 awarded by the Bankers’ Almanac, Britain
· Number
1 bank of Nepal-2003 awarded by the Bankers’ Almanac, Britain
· National
Excellence Award- 2003 awarded by federation of Nepal chambers of Commerce and
Industry.
All Branches of HBL are integrated
into T-24, the single Banking software where the Bank has made substantial
investments. This has helped the Bank provide services like ‘Any Branch Banking
Facility’, Internet Banking and SMS Banking. Living up to the expectations and
aspirations of the customers and other stakeholders of being innovative, HBL
very recently introduced several new products and services. Millionaire Deposit
Scheme, Small Business Enterprises Loan, Pre-paid Visa Card, International
Travel Quota Credit Card, Consumer Finance through Credit Card and online
TOEFL, SAT, IELTS, etc. fee payment facility are some of the products and
services. HBL also has a dedicated offsite ‘Disaster Recovery Management
System’. Looking at the number of Nepalese workers abroad and their need for
formal money transfer channel; HBL has developed exclusive and proprietary
online money transfer software- Himal RemitTM. By deputing our own staff with
technical tie-ups with local exchange houses and banks, in the Middle East and
Gulf region, HBL is the biggest inward remittance handling bank in Nepal. All
this only reflects that HBL has an outside-in rather than inside-out approach
where customers’ needs and wants stand first.
HBL's VISION
To become a "Leading
Bank of the country" by
providing premium products and services to the customers, thus ensuring
attractive and substantial returns to the stakeholders of the bank.
HBL's MISSION
To become preferred provider of quality financial services
in the country. There are two components in the mission of the Bank; Preferred Provider and Quality
Financial Services; therefore HBL believe that the mission will be
accomplished only by satisfying these two important components with the
customer at focus. The bank always strives positioning itself in the hearts and
minds of the customers.
HBL’s Objective:
"To become the Bank of first
choice" is the main objective of the
Bank.
3.2 Equity Structure of HBL
The Equity structure of Himalayan Bank has been briefly summarized in the
table
below:
Table 3.1: Equity
structure of HBL
|
Equity
|
Amount (in Rs.)
|
|
Authorized Capital
|
2,400,000,000
|
|
Issued Capital
|
1,600,000,000
|
|
Paid up Capital
|
1,600,000,000
|
Source: HBL Annual
Report 2009/10
3.3
Share composition of HBL
The table below shows the share ownership of HBL.
Table 3.2: Share
ownership of HBL
|
Local Promoters
|
51%
|
|
Foreign Partners (Habib)
|
20%
|
|
Employee Provident Fund (EPF)
|
14%
|
|
General Public
|
15%
|
3.4 Organization Structure of HBL
Himalayan
Bank Limited has a very typical organization structure where the top level
management includes the CEO, Senior GM and GM. Under them are the various
departments of the bank with one person heading each department. The major
decisions are taken by chief Executive Committee. The organizational structure
of Himalayan bank is shown below:
3.5 Board of Directors in HBL
Himalayan
bank is managed by a team of professional Board of Directors. The Board of
Directors consists of the brilliant personalities assigned with various
designations. The name list of BODs along with their designations is placed in
annex 2.
3.6 Corporate Social Responsibilities by HBL
HBL is not only a bank; it is a committed corporate
citizen. Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) holds one of the very important
aspects of HBL. Being one of the corporate citizens of the country, Right from the
time of its commencement, it has been discharging its social responsibilities
through various social and allied institutions. Being one of the active and
responsible corporate citizens of the country, HBL has always promoted social welfare
activities. Many activities that do a common good to the society have been
undertaken by HBL in the past. HBL is enthusiastically interested in enrolling
itself in such activities on an ongoing basis. The major services being
rendered by HBL in this front include those related to education, healthcare,
sports, culture and social services. HBL allocates a significant portion of its
‘Annual Sponsorship & Donation Budget’ for fulfilling social
responsibilities.
HBL CSR Activities:
- 2012: Financial Aid to
“PourakhiBalSikshyaKosh” to meet the education expenses of 10 children who
are barred from education.
- 2012: On the occasion of 19th
anniversary of Himalayan Bank, HimalRemit, under its corporate social
responsibility, distributed solar lanterns to local people of Salme VDC,
Nuwakot District, and the village which is yet to get connected to
national electricity distribution line.
- 2012: HimalRemit has
contributed to help Birendra Higher Secondary School, Pakuwa-6, Parbat
Dist. to rebuild its damaged building by a natural disaster. On the
occasion of 19th anniversary of Himalayan Bank, CEO Mr. Ashoke SJB Rana
handed over the contribution amount cheque to the principal of the school
Mr. Rudra Bahadur Rimal. The newly rebuilt building of the school was
inaugurated by General Manager of Himalayan Bank, Mr. Sushiel Joshi in a
ceremony held in the school premises on 21st June 2012.
- 2012: HimalRemit in
association with its principal agent CFS, distributed relief needs (rice
and lentil) to the appx 500 fire-victim families of Aurahi Village,
Siraha.
·
2012: HimalRemit provided Rs.
84,000 to the widow of deceased Dil Bahadur BK of Pipaltari-9, Parbat as a
small support to her daily needs. The amount will be availed in installments of
Rs 7,000 per month. Dil Bahadur BK, the only support to the family, was killed
in a road accident in Saudi Arabia.
3.7 Products and Services of HBL
A.
Deposit product
|
·
Fixed
deposits
·
Current
account
·
Normal
saving account
·
Bishesh
Saving Account
·
Recurring
saving account
·
Himal
saving account
|
·
Call
Account
·
Premium
saving account (PSA)
·
Super
premium saving account
·
Shareholder’s
saving account
·
Jumbo
Term deposits
·
Himal
remit saving account
|
B.
Loans
Loan facilities provided by HBL are:
1.
Corporate Loan
Corporate loan of HBL is classified
in two categories. They are:
|
Funded Facilities
·
Project
/ Consortium Loan
·
Non
Revolving Cash Credit
·
Working
Capital Financing
·
Overdraft
Facility
·
Demand
Loan
·
Revolving
Cash Credit
·
Import
Credit for Telex Transfer and Demand Draft Payment
·
Trust Receipt
Loan
·
Export
Credit Facilities
·
Pledge
Loan
·
Clean
Bills purchased and discounted
·
Documentary
Bills Purchased and Discounted
|
Non- funded facilities
·
Bank
Guarantee
·
Letters
of Credit
|
|
2. Retail/ Consumer Loan
·
Hire
Purchase Loan
·
Housing
Loan
·
Subidha
Loan
·
Credit
Card Loan
·
Loan
against Fixed Deposit Receipt
·
Loan
against Government Bonds & Bonds of Bank
·
Loan
against First Class Bank Guarantees
·
Loan
against Shares
|
3.
Small
and medium enterprises loan
(SME Loan)
Funded/Non-Funded
Facility in range of Rs. 0.5 M to Rs. 40.0 M
|
C.
International Banking (LC)
To assist its trading customers, HBL offers Letter of Credit (LC)
facilities. Customers can place their LC application in any of HBL branches.
The fees/ charges are one of the lowest amongst the commercial banks of Nepal.
The customers enjoy wide correspondent network of HBL in addition to attractive
rates.
D.
HIMAL Remit
Himalayan Bank Ltd. is a
pioneer in the field of retail money transfer business with over a decade long
customized service delivery experience in the field. HimalRemit is a
state-of-the-art web-based online money transfer system. It is easily
accessible through website of HBL. It can be directly accessed by all branches
and network thus ensuring prompt execution of the remittance. The product is
monitored and serviced 24/7 by Remittance Promotion Department of HBL dedicated
to deliver fast and reliable services to the customers. Himal Remit has the
largest payment network covering all cities, towns and villages of the country
and is capable of paying at more than thousand locations across Nepal which is
in ever growing trend as per the demand of local customers and service
providers.
E.
Safe Deposit Lockers
Looking at
the varying needs and wants of the customers, HBL offers locker facilities of
various sizes as per customer’s preference and convenience of location.
Customers availing of this facility enjoy not only peace of mind in terms of
security of their valuable belongings but also one of the most attractive rates
and ease of location.
Salient
Features:
· Temporary
Locker Facility for client Going Abroad Period: 3 months to less than 6 months
50 percent of annual charge
· Temporary
Locker Facility for client Going Abroad Period: 6 months to less than 1 year 75
percent of annual charge
· 25
percent Discount on Annual Rent to PSA Holders
· 100
percent rebate on key deposit and 50 percent on annual rent to HBL board of
members, chairman, advisor to BODs, staffs and their spouse.
F.
Cards Services
HBL provides various card facilities to the customers can withdraw cash
as well as purchase goods from several merchants. Customers use these cards at
any ATM terminal of HBL networks as well as SCT network also. HBL provides ATM
services to their customer, which is open 24 hours, a bay, 7 days a week, and
365 days a year. The cards facilities by HBL are:
·
ATMs
Card
·
Credit
Card (VISA/Master card)
·
Prepaid
Card
·
VISA
Debit Card
·
Master
card
G.
SMS Banking and E-Banking
SMS Banking
allows customers to check their balance, status of cheque (encashed or not),
HBL’s foreign exchange rate and contact numbers of branches. Through the
customer service department customers fill up the application form to apply for
these services. After fulfillment of the application form, the information
regarding customer are sent to the information department for further process.
After that pin number issued by the information department is provided to the
customer through the customer service department. By using E- Banking and SMS
Banking customer can make inquiry for balance and can get the mini statement by
using the electronics means and mobile by suing SMS.
3.8 HBL Branches and Networks
HBL have totaled 41 Branch
networks including branches inside and outside the valley which does
operational activities of the banks. Corporate office located at Kamaladi,
Kathmandu does all the management activities only. There are 40 ATM locations
inside Kathmandu valley and 26 outside Kathmandu Valley.
CHAPTER FOUR
ANALYSIS OF
ACTIVITIES DONE AND PROBLEM SOLVED
4.1 Introduction to
bills and remittance:
Remittance
in general means transfer of money from one place to another place. Bills and remittance department is concerned
with fund transfer, throughout the country and world, currency exchange,
issuance of draft, telex transfer, advance payments, collections and clearance
of cheques. Remittance is the flow of money from one economy to another, which
is sent by migrant workers. It can be both internal and external. Remittance
creates multiplier effect in domestic country. Money coming through remittance
increases investment and saving. Remittance also has positive effect on balance
of payment.
Generally, remittance
refers to that portion of migrants earnings sent from the migration destination
to the place of origin. Even though they can also be sent in kind, the term
‘remittance’ is normally limited to monetary and other cash transmitted by
migrant works to their families and communities.
Remittance
business was created by the foreign employment. These remittances are generally
used to cover day to day living expenses, to provide a cushion against
emergencies and making small investment. In developing countries like Nepal,
these remittances noticeably exceed foreign direct investment (FDI).therefore
the government should pay more and more attention in developing appropriate
strategies to remittance flows as important financial sources to boost economy
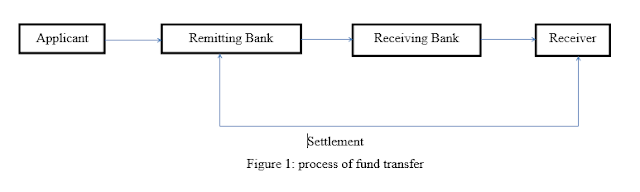
development. Simple process of fund transfer can be shown through following
figure:
Figure 1: process of fund transfer
4.2 Types of Bills and Remittance:
The remittance can be divided into inward and outward remittance.
Similarly the bills can also be divided into same types.
4.2.1 Inward:
Funds being received in
Nepal from other countries are termed as inward remittance. The procedures are
discussed later in this chapter.
The HBL cheques that
customers has deposited in different other banks within the country are
collected through ECC. This is known as inward clearing. Cheques of HBL are
collected that has been deposited in various banks within city or in different
locations in the country. Similarly the cheques of HBL are deposited in
different foreign banks and this takes time to receive by the HBL, this is
inward collection.
4.2.2 Outward:
Funds being transfer to
other countries from Nepal in different means and purpose are known as outward
remittance.
Cheques of different
banks of the same cities in Nepal and from other locations are received in HBL.
These needs to be sent to the respective banks for clearance purpose and are
entered in the ECC with the details of the cheque. This is known as outward
clearing. Likewise various foreign banks’ cheques are received and being
impossible for clearance purpose, are collected and sent to the respective
banks through dispatch department. This is known as outward collections.
4.3 parties involved in Remittance:
While remitting the funds from one place to another, following
intermediaries plays crucial roles:
Remitter: Persons sending the money.
Remitting Bank: Remitters’ bank which
receives money from remitters and
Sends
the funds.
Paying Bank: Bank that receives message from remitting banks and
pays to the beneficiary.
Beneficiary: A person who is intended to receive money.
4.4 Instruments of Bills & Remittance department:
The instruments used in bills & remittance department of HBL are as
follows:
4.4.1 Demand Draft (DD):
A demand draft is an
instrument, which is drawn by one bank upon another bank for a specific sum of
money payable on demand. It is made by the bank and given to the purchaser
against cash or cheque. If two banks two banks are involved, then one bank
sends a DD to another bank. But in customer-bank case the customer sends
his/her DD to the receiver.
Demand draft is the bill
of exchange or cheque or drawn by bank in the name of the person or institution.
Amount of draft is paid to the person or institution through beneficiary bank.
Demand draft is cost effective as compared to other means of transfer.
Basic element of
draft:
Date: date on which draft has been
issued.
Drawer: issuing bank.
Drawee: bank on whom the draft has been
drawn.
Payee: final receipt of the proceeds of
the draft.
4.4.2 SWIFT transfer:
SWIFT stands for Society for Worldwide Inter-Bank Financial
Telecommunication, which was established in 1973 by 239 banks of 15 countries.
It is a bank owned cooperative society for transmitting financial message.
SWIFT is a reliable and effective communication network in terms of speed,
accuracy and security. It covers transactions like customer transfer,
documentary letter of credit cards, collection, FOREX confirmation etc. There
is no need of having an account with banks for fund transfers through SWIFT.
Funds can be received and transferred virtually anywhere in the world. Thus,
SWIFT can be taken as the modified version of TT messages.
HBL has established separate department as SWIFT since it has
various purpose in banking business. Bills and Remittance Department has a good
co-ordination with the SWIFT department.
4.4.3
Traveler’s cheque (TC)
Traveler’s cheques are used instead of
carrying cash. People prefer to carry TC for safety reason. Americans express
TC is available for sale. TC is in the nature of prepaid cheques issued by the
banks in a designated currency in fixed denomination cashable at a wide range
of location. At the time of encashment, the person has to sign in encasing
place and fill in the relevant data. Most well-known banks in the world have
issued TC in different currency.
4.4.4
Manager’s Cheque (MC):
It is a cheque drawn by HBL on itself,
especially used for payments made by HBL itself. Beneficiary can send the
cheque on collection and clearing or can deposit it customers’ account with HBL
itself. MC is one of the most secured modes of payment with primary liability
being that of issuing bank. It is ideal for making payments within country or
simply for transferring fund between the cities.
4.4.5
Telex Transfer (TT):
Telex Transfer is sometimes known as
telex telecommunications. It is the instrument for transferring the funds
quickly and securely within the country or anywhere in the globe. In TT, fund
is transferred electronically on the same day or next working day or with a
forward value date. HBL has facilitated customers in sending and receiving
funds by means of TT.
4.4.6
Collection:
Another important instrument of HBL
Bills & Remittance Department is collections. Cheques of various
international banks are dealt and the process is called collections. Collection
is similar to clearance of cheques. Various cheques of international banks in
various parts of world are difficult for clearance purpose so collection method
is used. In collection, cheques of different foreign banks and thoroughly
checked including its amounts, endorsements and stamps. After all required
verification they are sent to their respective banks and amounts are debited or
credited accordingly. The collection of HBL cheques from various countries is
inward collection and sending cheques of different banks around the world to
their respective destination is called outward collection.
It is difficult or nearly impossible to
establish clearing house for collection purpose. Thus for this the concept of
nostro and vostro account is essential elements of collection.
Nostro
accounts
HBL accounts maintained at the book of
other banks are Nostro accounts and corresponding accounts maintained at HBL’s
book to reflect of the activities of these Nostro account is termed as mirror
account.
Vostro
accounts
Other banks account maintained at the
HBL are termed as Vostro account. For example HBL’s USD account maintained at
Amex NY is Nostro account for HBL and same account is Vostro account for Amex
NY.
4.4.7
Clearance:
Modernizing
the Banking sector in Nepal is an essential strategic objective that Nepal
Rastra Bank seeks to realize by implementing an advanced cheque clearing
solution that manages the daily cheque clearing cycle electronically.
ECC is the state-of-the-art interbank
cheque clearing solution that has replaced the manual cheque clearing solution
in Nepal. It is an image-based, cost-effective, cheque clearing and settlement
solution, where the original paper cheques are transferred to scanned images in
order to be presented electronically through the secured communication channels
from the member in which they are deposited to the member on which they are
drawn resulting in a faster access to funds, lower transportation expenses and
increased cheque trust.
ECC calculates the multilateral net
clearing position and sends to the Settlement System of Nepal Rastra Bank for
settlement of the net clearing position of the direct member. The Central
System of the clearing mechanism lies at Nepal Clearing House Limited.
The
Clearing House main activities can be summarized as the following:
1.
Receiving cheques from presenting members for
outward clearing, and assuring the presented cheques validity.
2.
Transmitting cheques to respective Paying members for inward clearing
3. Receiving replied cheques and rejected
cheques from paying members
4. Transmitting replied cheques and returned
cheques to Presenting members.
5. Ending the clearing session of the current
business day.
6.
Generating the Net Clearing Position (NCP) and submitting the file to
NRB for settlement through the direct members’ accounts.
7. Starting a new clearing session.
4.8 Functional sections of remittance
department:
4.8.1
ID Payment Section
ID payment is the process of providing
cash to the customer that is received through remittance after verification of
receiver. It is a transfer of
money by a foreign
worker to his or her family or making domestic
payment. HBL has facility for both international payment (For Eg: Himal Remit
of HBL) and domestic payment (Domestic Money Transfer (DMT) facility by HBL).
The activities done in ID payment are:
· Entry
of rad no. on web based remit system to get remittance information under
various exchange houses such as Himal Remit, Western Union Money Transfer,
Money Gram, Choice Money Transfer, etc.
·
Verification
of the information of the remitter and beneficiary.
·
Photocopies
of customer Id
·
Recording
of remittance information
·
Forwarding
the verified information for cash payment.
·
Contacting
authorized personnel if problem arise.
4.8.2
Bills Collections Section
It does the all tasks related to
international banks cheque, traveler's cheque (TC) i.e. making TC and bills
purchase and collection, entry on Nostro and Vostro account, sending to
international bank about payment against TC, etc.
The activities done in bills collections are:
· Manual
entry of Traveler's Cheque, international cheques collection and purchase in
registers.
· Observation
of procedures for forwarding Traveler's Cheque.
· Stamping
Traveler's Cheque that are purchase and collected which are to be presented to
Americans Association for Traveler's Cheque.
4.8.3 Advance Payment of Credit Advice (APC) Section
APC does the transaction related to
transferring of funds from one account to another account but only receivable
of information of credited account that is done through SWIFT mechanism. It is
basically used by customer involved in exporting goods to receiver advance
payment for making supply.
The activities done in APC are:
·
Informing
customer about account credited.
·
Print
account movement advice and account payment advice.
·
Checking
statement of customer related to fund transfer.
·
Filing
of the bank copy of APC.
·
Observation
of account to account transfer entries by the employee.
4.8.4
Fixed
deposit and Fund transfer Section
i.
Fixed
deposit
Fixed deposit is the process of depositing
money that pays higher interest than a savings account but imposes conditions
on the amount, frequency, and/or period of withdrawals. It is also called time
deposits. Transaction related to fixed
deposit account of HBL were carried out by remittance department.
ii.
Fund
Transfer
It is transfer of fund from one place to
another through demand draft or telex transfer. Demand draft is a written payment order
from one party (the drawer) to
another (the drawee to pay a stated sum to a third party (the payee) by
issuing the cheque. Telex transfer is the mechanism in which bank transfer the
fund to another banks account in the request of customer. For e.g. Fees payment
of student reading abroad is done by telex.
The activities done in fixed deposit and fund transfer are:
·
Providing
different kinds of forms to customer such as demand draft forms, telex transfer
forms, fixed deposits forms, etc.
·
Filing
application forms and writing different application on behalf of customers on
the request of customers.
·
Recording
of fixed deposits account, demand draft transfer, and telex transfer, etc. in
the registers and filing the documents.
·
Writing
in the cheques using Cheque Writer.
·
Observation
of record keeping in the HBL software system (T24 software) by the employees.
4.8.5 Clearing Section
Clearing
section is one of the counters under the bills and remittance department where
both the inward and the outward cheques are handled. An individual might
receive payments via cheques of various banks. ECC (Electronic Cheques
Clearing) is a software mechanism that brings together all its members
(financial institutions) for clearings of the cheques. The cheques of those
financial institutions that are not the member of ECC are cleared in the
clearing section of the NRB.
The activities done in
clearing section are:
·
Receiving
the cheque for clearing and endorsing the cheque
·
Making
entry in the Globus system for clearing
·
Informing
the client in case of cheque return
·
Returning
the rejected cheque to the respective clients and maintain proper records
·
Handling
queries of the customer
·
Returning
the rejected cheque to the respective clients and maintain proper records
·
Handling
queries of the customer regarding their cheques sent for clearing.
·
Going
NRB for observation of clearing procedures carried out by banks.
CHAPTER FIVE
Conclusion AND lessons learnt
5.1 Conclusion
An internship
course of BBA has its own significance, which makes the students to complete
graduation in real world exposures of theoretical knowledge. Internship
provides the opportunity of gaining the practical knowledge and observing the
real application of theoretical aspects. Some facts about the privacy and
systematic approach of the organization were revealed. Internship has helped to
explore the fundamentals of baking system.
Coordination and
integration of various departments in banking systems is a must. Banking
organization is divided into various functional areas which are interlinked,
interconnected and interdependent with each other. If there are no team efforts
then no organization can achieve its organizational goals. Therefore, there
must be cooperation and support within the staff of the overall functional
areas to be successful.
The bank should
value the customer needs and solve the problems as soon as possible as tight
competition between them is taking a massive form. This helps to retain and
maintain existing customer by providing service up to their expectations. It
should take various customer feedbacks and provide them prompt and convenient
services. These were observed as an intern in HBL.
HBL has been
successful to create its own image within the country, and it is also
successful to create the banking relation with the most of the countries of the
world. It is capable to render its services necessary for export and import to
any businessperson of the world. Himal remit is an innovative product of HBL
and is being facilitating the customers as to match up their expectations. HBL
is playing a leading role in banking industry through its innovative products
and services that match the customer’s expectations.
5.2 Lesson Learnt
This internship report is based on
internship done at HBL, Thamel Branch from June 15, 2012 to August 13,
2012 to know the various
processes and working environment of banking in real life. I have gained lot of
experiences from the internship in HBL, which was my first experience in
banking sector. This internship program helps me to learn professional attitude
for future prospects and to learn practically apart from academic courses.
During this period, I was able to learn different services and products that
are delivered by bank, organizational culture, nature of organizational
problems, etc.
The lessons learnt are as follows:
·
Learnt about general banking operations.
·
Learnt overall basic functioning of the bank.
·
Learnt to co-operate in work place and to coordinate
the efforts of five sections of remittance department.
· Learnt to make good relations with co-workers,
seniors, corporate clients and general customers.
·
Learnt to adjust own self in various working
environment.
·
Learnt to adjust with the official norms.
·
Learnt to perform various activities
assigned.
·
Learnt how professionalism develops.
·
Learnt about the inter-relation and integration
of various departments in banking system.
·
Learnt general systems used in banking
information technology.
·
Learnt basics about NRB directions regarding
commercial banks.
· Learnt about authority and responsibility
relationship among various managerial and subordinate level in the hierarchy of
commercial banks.
·
Learnt about the overall norms and
organizational behavior regarding HBL.











EmoticonEmoticon