Internship Report on Civil Bank Limited (CiBL), Nepal
CHAPTER
ONE
INTRODUCTION
1.1 Background
The scope of BBA has
grown as an important academic discipline with practical dimension. This has
grown according to needs of the institutions with the growth of financial
sectors in particular and other professional organizations in general.
In the present day world,
people are becoming more knowledge oriented in relation to practice in the real
life situation of problem-solving. Due to this reason, many schools and
colleges are emerging year by year. Among the various universities, Tribhuvan
University (TU) is the largest and oldest university of Nepal. Bachelor in
Business Administration (BBA) is one of the demand driven management courses
among different management courses of TU to makes students not only brilliant
in the pursuit of knowledge but also practical to behave in the decision-making
process.
BBA is 4 years complete
program course of making students eligible for BBA degree and this program is
instituted to develop socially responsible, creative and result oriented
management professionals to fill up the middle-level managerial positions in
the rapidly growing business sector in Nepal as well as aboard. The interest in
BBA is increasing day by day because it is accepted worldwide as it covers the
International standard of four years (one hundred and twenty credit hours)
course in developing professionalism to make the students of today as the
future stars of the nation building.
Moreover, students studying this course are evaluated on the basis of
the grading system and it has a facility of semester system which includes 8
semesters. A single semester is completed within six months.
1.2 Importance of Internship
Since theoretical
knowledge is not sufficient in this competitive environment, in the 8th
semester of BBA program, students are required to work in the financial
institution for at least eight weeks where they can experience real work
environment. It also helps in understanding organizational environment and
culture. Internship program enables in acquiring skills and techniques by experiencing
practical work situations directly applicable to develop the career on
financial sectors. In some situation, internship program also helps in getting
the job in host organization or other organization.
1.3 Objectives of Study
Every action is directed
towards accomplishing certain objectives. The objectives are the things that we
are planning to achieve. It may be things, skills, qualities, knowledge etc.
Setting objectives helps to understand and analyze how our actions need to be
directed. It basically helps to answer the question how to achieve our larger
target. Well, internship program is in itself a new learning pedagogy which
provides the floor for the practical exposure of theoretical knowledge,
however, the objectives of the study and making the report are:
• To understand how theoretical concepts are
implemented practically in the working procedures of financial institutions
• To understand the banking organization, its
structure, culture, norms, working procedures and risk associated with it
• To attain the performance done and gain skills
in handling functions of different Department of Banking industry
• To gain knowledge on functioning of credit
department of commercial bank
1.4 Methodology
1.4.1
Organization Selection and Placement
Being a BBA student
specializing in “Finance”, doing an internship in “A” class financial
institution is always in a top priority. Nevertheless, selecting an
organization has been a tough job because much of time was spend on searching
the right institution for me. Internship from a reputed financial institution
helps to build the career by creating linkage between classroom knowledge and
practical business world experiences. So by going with the trend, I applied for
the internship in some financial institutions. Fortunately, I got an
opportunity to work in civil bank limited.
1.4.2
Duration of Internship
The duration of
internship has been defined for the minimum of eight weeks. The internship was
conducted from 4th June 2012 to 3th August 2012 under the supervision of Mrs.
Sharmila Bista, Credit Department Head, and New Road Branch. During my 8 weeks
of internship, I was assigned to work in the following department:
Table
no. 1.1: Duration of internship
Name of
Departments
|
||||
No.
of weeks
|
CSD
Department
|
Marketing
Department
|
LC
Department
|
Credit
Department
|
1-2
|
||||
3-4
|
||||
5-6
|
||||
7-8
|
||||
1.4.3
Sources of Data Collection
Sources of data
collection refer to the way of acquiring the related information from different
sources. By directly involving in the banking institution as an intern the
following primary sources and secondary sources of data collection:
Primary
Source:
• Direct personal interview with the related
staffs
To collect the necessary
information for this report asked many structured, unstructured and practical
questions to the relative staffs of the branch.
• Unstructured
interview with the clients
Clients are also the
source of information and they provide the information based on their
perception towards the products and services. Visiting of different clients for
marketing purpose helps a lot for acquiring information and perception from
existing clients about the bank products and services.
Secondary
source:
• Visited the various web site of civil bank
and other commercial banks
• The articles and magazines are the other
secondary source through which necessary
information are acquired
• The brochures and the annual report of
Civil Bank Ltd
1.4.4
Activities Performed in the Civil Bank Limited
This section includes the
study based on the internship period and the various tasks performed during the
stay in the bank for 8 weeks. The following are the activities which interne
performed, as an intern, in the bank:
Credit
Department:
• Prepared checklist of original documents
and other necessary documents while providing loan
• Filled missing information of clients in
the documents
• Checking property details of clients
• Observed the process of verification of
name and address of SME customers, limit, area of mortgaged property in the
mortgage deed with that of ‘Lal Purja’ provided by customer
• Checking whether the Current market Value
or Distress Value in the valuation report is sufficient to meet the limit
• Stock visit of the clients
• Calculate various ratios from the provided
balance sheet and income statement for analyzing the health of the firm
Customer
Service Department:
• Account opening (Personnel and Corporate)
• Issuance of Debit card and cheque book
• Balance inquiry and other information about
the bank service
• Providing information about products to the
customers
• Issuing of account statements and balance
certificate
• Solving the queries of the customers.
Letter
of Credit Department:
• Providing Forms of Letter of Credit
• Checking documents like: invoice, packing
list, legal documents, date of shipment etc
• Doing photocopies, fax, scanning of
documents
• Filling the Bi.Bi.Ni.Fa.No.4
• Keeping records of documents received
manually
• Preparing
NRB checks
• Recording of documents received from the
sender of goods
• Filing of documents according to LC no. and
branch code
Remittance
Department:
• Observe the procedures for fund transfer in
domestic and international network
• Help the customer to fill their form for
receiving the money as well as sending money
• Observe the procedure for preparing drafts,
managerial checks, travelers check, outward clearing of checks
• Help the customer for opening fixed deposit
in the bank
Marketing Department
• Dealing with customers directly for
acknowledging them about the banking products and services
• Participate in new loan product survey
namely “SME loan survey” at Peoples Plaza, and Pashupati Plaza.
• Visited various Gold account Customers to
inform about new product of the bank
1.5 Scope of the Study
The scope of the
undertaken project is supposed to be wider in terms of the following points:
• Expansion of the horizon of knowledge of
interns
• Practical learning through the exposure of
various task related activities
• Helps in shaping the future career
1.6 Limitation of the study:
Despite most of the
efforts undertaken to make my project more realistic, practicable in terms of
Nepalese context, there are certain limitations of my study:
• Internship time period was not sufficient
enough to gain much of banking knowledge
• Information about the banking business is
strictly confidential
• The access to the system is strictly
prohibited to the interns
• This study may not be applicable to other
organization of similar nature
CHAPTER
TWO
INTRODUCTION
TO THE INDUSTRY
2.1
Introduction of Bank
A bank may be defined as
an institution which deals in monetary transaction. It is a financial
intermediary which works as a bridge; fills the gap of fund between lenders and
borrowers (entrepreneurs). Bank draws surplus money from the people who are not
using it at the time (having excess money) and lend to those who are in a
position to use it for productive purposes. It creates credit and also provides
exchange facilities to the public. the So, bank is also known as a factory of
credit production.
The bank pays a certain
amount of money as interest, on the money they have borrowed. Similarly, they
charge interest on the money lent. Interest is always calculated in certain
rate percent per annum. The rate of interest on loans advanced is always
greater than that on deposits. The difference between the two rates is the
bank’s margin of income.
Some definitions of banks
are:
“Bank is a financial
institution, which provides financial services that may be in the form of
accepting deposits, advancing loans, providing necessary technical advice,
dealing over foreign currencies, remitting funds, etc.”
Nepal Rastra Bank Act
2002
“Banks are financial
institutions that fund in the form of deposits, repayable on demand or in short
notice.”
World Bank
From the above
definitions, it is clear that a bank is a financial institution, which accepts
deposits from the public in different accounts and grant loans to individuals
and corporations against their certain securities. In these days, it performs a
wide variety of functions. It does lot more than deposit and credit such as
remitting money, letter of credit, guarantee, etc, for the service and benefits
of individuals, corporations and general public .i.e. it is an agent of its
clients, which remits money, provides services like LC, guarantee etc. and
collects incomes, commissions and pays expenses on behalf of them.
2.2
Origin of Bank
The banking concept is as
old as authentic history. The word ‘bank’ is derived from the Latin word
‘bancus’ which means bench. In the ancient time, the Italian goldsmith used to
sit on the benches when they were in work of exchanging of money; trading of
gold and silver. The word bench means ‘Banck’ in German, ‘Benca’ in Italian and
‘Banquee’ in French, from which it is used as ‘BANK’ in The English Language.
The following functions
were in use even in the second millennium in Babylonia, but the deposits were
not of money but of cattle, grain or crops and eventually precious metals.
Nevertheless, some of the basic concepts underlying in today’s banking system
were present in the ancient arrangements. Deposits were accepted, loans were
made and borrowers paid interest to the lenders.
The history of modern
banks starts from the establishment of Bank of Venice, established in Venice,
Italy in 1157 AD. Subsequently, Bank of Barcelona (1401) the and bank of Geneva
(1407), Bank of Amsterdam (1607) the and bank of Hamburg (1619) were established.
The ‘Bank of England’, first English Bank, was established in 1964 A.D. The
bank of Hindustan established in 1770 A.D. is regarded as first bank in India.
But these banks were not established according to law. In 1833 A.D., Banking
Act 1833 was introduced in United Kingdom which allowed operating Joint Stock
Company Banks. With the expansion of the commercial activities in the northern
Europe, there sprang a number of private banking houses in Europe and slowly
spread throughout the world.
2.3
Importance of Bank
The Bank accepts deposits
of spare money from its customers. The deposits are utilized the for
formulation of capital in the productive sectors like industry, trade and
service area of the country. The bank issues different types of credit instrument
such as bank draft, letter of credit, credit cards and telegraphic transfer
(T.T.). These credit instruments facilitate fast and safe remittance of money
from one place to another.
• Banks finance priority sectors, thus
helping in economic development of the country
• Bridge the gap between surplus and deficit
unit.
• It offers different types of loans and
advances enabling manufacturers to undertake new ventures, adopt new techniques
and introduce new means of production
• It provides various card services, which
has eliminated the difficulties and risks of carrying
• Facilitate the customers with new and
advanced products
2.4
Banking Sector in Nepal
The history of Nepalese
banking industry is not so long. The origin of modern banking dates back to the
ancient times. However, in the context of Nepal, the concept of modern banking
has emerged recently.
Modern banking system in
Nepal started from the establishment of Nepal Bank Limited (NBL) in 1937 A.D.
under “Nepal Bank Act, 1937”. It is the first bank in Nepal. Nepal Rastra Bank,
the Central Bank of Nepal, was established in 1956, to discharge the central
banking responsibilities including guiding the development of Financial Sectors
in Nepal. Another commercial bank, Rastriya Banijya Bank (RBB), was established
in 1965 A.D, realizing NBL alone couldn’t extend adequate service to the
country in terms of commercial banking. After the establishment of RBB, no new
commercial bank was established for a period of nearly 18 years.
To promote healthy
competition among banks, commercial Bank, Act 1974 was amended in 1974. The new
policy allowed joint venture banks with foreign collaboration to operate in
private sector with the objective of introducing modern banking practices and
widen the financial structure. With the introduction of this policy, different
commercial banks were established.
Financial sectors in
Nepal have become one of the major contributors to the Nepalese Economy. There
has been a rapid growth in the Financial Institutions in the recent years. The
present scenario of Nepalese Financial Institutions can be presented as:
Table
no. 2.1: No. of financial institution in Nepal
Type of Financial Institution
|
Class
|
Number
|
Commercial Bank
|
A
|
32
|
Development Bank
|
B
|
83
|
Finance Companies
|
C
|
79
|
Micro Credit Development Banks
|
D
|
19
|
Saving and Credit Co-operatives (Licensed by NRB)
|
N/A
|
16
|
Non Governmental Organization (Licensed by NRB)
|
N/A
|
45
|
Total
|
274
|
|
(Source: www.nrb.gov)
2.5
Introduction of Commercial bank
A commercial bank is a
type of financial institution and intermediary. It is a bank that provides
transactional, savings, and money market accounts and that accepts time
deposits.
It is an institution
which accepts deposits, makes business loans, and offers related services.
Commercial banks also allow for a variety of deposit accounts, such as
checking, savings, and time deposit. These institutions are run to make a
profit and owned by a group of individuals. The number of Commercial Banks has
increased from 25 in 2009 to 32 in 2012, offering wide varieties of products
and services.
2.5.1
The Role of Commercial Banks
The modern commercial
banks have played the major role in every sector of the economy. The role of a
typical commercial bank can be explained with the figure as follows:
Figure
no.2.1: Role of commercial banks
2.5.2
Growth rate of commercial bank in Nepal
The development of
commercial banks in Nepal and their growth rate can be explained with the
figure as follows:
Fig
no.2.2: Growth rate of commercial bank in Nepal
The above figure clearly
explains the growth rate of the commercial bank in Nepal. With the increase in
no of the commercial bank, the competition among the firm is also increasing
year by year.
CHAPTER
THREE
INTRODUCTION
OF THE ORGANIZATION
3.1
Background
Civil Bank Limited (CiBL)
has established itself as the 30th commercial bank of Nepal. It is founded by
promoters with the strong background in real estate, financial institutions,
business, trade, and industry. The Bank envisions in becoming a dominant player
in the Nepalese banking industry.
The Bank has been
registered with an issued capital of NRs. 2000 million and paid up capital of
NRs. 1200 million. The Bank firmly believes in contributing to the nation's
economic growth by rendering services and empowerment to all classes and
sectors of the society. Recently this bank has been running with its 13
branches located at different parts of Nepal.
3.1.1
Vision of CiBL
To become the most
trusted bank by providing dedicated service and support to customers through
thick or thin.
3.1.2
Mission of CiBL
To become every Nepali's
banking partner by extending all types of banking services.
3.1.3
Goal of CiBL
To contribute
directly/indirectly in the economic growth of the country by being a prominent
player associated with all classes and sectors of society.
3.1.4
Objectives of CiBL
• Prudent expansion
• Innovation
• Dedicated customer service
• Competitive human resource
• Vigilance
With the two major
slogans, one bank 20 million aspirations and thinking forward moving forward,
CiBL has been moving forward to make its own different and renowned status in
the banking industry.
Similarly, the bank bases
itself on a set of superior values and moral principles. It aims to succeed and
reach higher grounds by maintaining and adhering to its corporate values.
The corporate values
governing Civil Bank's development include:
• Maintain the highest standards in all
relationships with customers, suppliers, environment and community.
• Foster a climate which encourages
innovation and diligence amongst staff and reward accordingly.
• Function with the principle of
"Thinking Forward Moving Forward".
3.1.5
Board of Directors (B.O.D)
The Board of directors of
CiBL consists of five members who have been elected for the proper execution of
banking activities and services. The board of director of Civil Bank consists
of promoters of Civil Bank. The name and designation of B.O.D are presented in
the annex.
3.1.6
Management Committee
Management committee of
CiBL consists of 20 people with their respective field of management is
presented in the annex.
3.1.7
Branch network
Civil Bank Ltd is trying
to reach maximum numbers customer by establishing new well-equipped branches in
different areas of Nepal. The Head Office of CiBL is located at Kamaladi,
Classic Complex, Kathmandu.
It has 13 branches all
over the country, 4 branches inside valley and 9 branches outside the valley.
The details about the branches are listed in the annex.
3.1.8 Equity structure of
CiBL
The CiBL is founded by
the promoters with the strong economic background. The bank has not issued its
share to the general public yet, but it has decided to issue the share to the
public amounting Rs. 80 million in the month of Mangshir. The current detail of
the equity of the firm is as follows:
Table
no.3.1: Equity Structure of CiBL
S
N
|
Equity
|
Amount
|
1.
|
Authorized capital
|
Rs.
4 billion
|
2.
|
Issued
capital
|
Rs.
2 billion
|
3.
|
Paid
up capital
|
Rs.
1200 million
|
The above table can be
presented in diagram as follows:
Fig
no.3.1: Equity structure of CiBL
3.1.9
Major indicators of CiBL
Table
no.3.2: major indicators of CiBL
Types of indicators
|
Relative rating
|
Earnings
per share
|
Rs. 0.10
|
Market
price per share
|
N/A
|
PE ratio
|
N/A
|
CRR
(Liquidity ratio)
|
24.25%
|
Weighted
average interest rate spread
|
2.5%
|
3.2
Product and services
3.2.1 Deposits
3.2.1.1
Saving accounts
1. Mero
Bachat Khata
Civil Bank Mero Bachat
Khata is an interest bearing normal savings account. This account intends to
develop a saving habit for the future in order to facilitate the accumulation
of funds over a period of time.
Criteria:
Minimum Balance: (No
minimum balance required)
Rate of Interest: 6.50%
per annum (On Daily Balance)
Withdrawals and Deposits:
Unrestricted
2.
Aama Buwa Bachat Khata
Civil Bank Ama Buwa
Bachat Khata is a special savings product designed for senior citizens. This
product not just yields high returns on the hard-earned income but also
provides them with convenience and easy accessibility to their savings account.
Criteria:
Minimum Balance: NPR
10,000
Rate of Interest: 7.75%
per annum (On Daily Balance)
Withdrawals and Deposits:
Unrestricted
Interest Posting: Monthly
Qualifying Age: 58 and
above
3.
Kishore Bachat Khata
Civil Bank Kishor Bachat
Khata is designed to instill a savings habit amongst parents so that can save
and amass the significant amount of funds to build a secure future for their
children.
Criteria:
Minimum Balance: NPR
1,000
Rate of Interest: 7% per
annum (On Daily Balance)
Withdrawals and Deposits:
Unrestricted
Qualifying Age: 16 and
below
4.
Nari Bachat Khata
Civil Bank Nari Bachat
Khata is a product especially for the ladies (housewives, professionals, and
others). This product is tailor-made to suit the requirements of its target
audience. This savings account offers exclusive value-added services.
Criteria:
Minimum Balance: NPR
1,000
Rate of Interest: 7% per
annum (On Daily Balance)
Withdrawals and Deposits:
Unrestricted
Qualifying Gender:
Females
5.
Gold Savings Account
Civil Bank Gold Savings
Account is savings scheme which offers an attractive rate of interest and is
for those individuals who are self-employed or professionals working in various
organizations. This scheme also gives the accountholder the added flexibility
of unrestricted withdrawal.
Criteria:
Minimum Balance: NPR 50,000
Rate of Interest: 8.50%
per annum (On Daily Balance)
Withdrawals and Deposits:
Unrestricted
6.
Silver Savings Account
Civil Bank Silver Savings
Account is savings scheme which offers a competitive rate of interest to the
accountholder and is for those individuals who are self-employed or
professionals working in various organizations. Besides offering an attractive
interest rate, the product is also flexible in that the customer can withdraw
and deposit funds as per their convenience while retaining the required minimum
balance in the account.
Criteria:
Minimum Balance: NPR
10,000
Rate of Interest: 7.50%
per annum (On Daily Balance)
Withdrawals and Deposits:
Unrestricted
7.
Civil Bank Loyalty Call Account
Civil Bank Loyalty Call
Account is meant for individuals and corporate houses who seek to earn interest
on their deposits on a daily balance as well as experience the flexibility which
the market today demands. Accountholders are paid interest on the daily balance
in their call account.
Criteria:
Minimum Balance: NPR
1,000,000
Withdrawals and Deposits:
Unrestricted
Account Type: - Loyalty
Current Account
Loyalty Call Account
Interest Rate
Calculation: Daily Basis
3.2.2
Loans and Advances
1. Personal Mortgage Loan
Civil Bank Personal
Mortgage Loan is one such product to cater to the various financing requirement
of individuals.
2. Home Loan
Civil Bank Home Loan is
established as a retail lending product to cater to the prevailing market
demands. CiBL 'Home Loan' limit shall be fixed for minimum and maximum range of
NPR 100,000 and NPR 50,000,000 respectively for all types of schemes.
3. Hire Purchase Loan
Civil Bank Hire Purchase
Loan (CiHPL) as a retail lending product to cater to the prevailing market
demands. Hire Purchase Loan will be applicable to private automobiles (cars,
jeeps), commercial vehicles (trucks, buses), heavy equipment (excavators,
cranes, dozers) and other equipment (hospital equipment, heavy kitchen
equipment).
4. Loan against Fixed Deposit Receipt
The Loan against Fixed
Deposit is an added feature in the Fixed Deposit product and enables the
depositor/accountholder to withdraw a certain percentage of the deposit as a
loan to cater his/her various immediate needs.
5. Loan against Government Bond/ Securities
Loan against Government
Bond/Securities enables an individual or firm to avail a loan against the value
of the securities and bonds in their possession.
3.3
PORTER’S Analysis of CiBL
Porter’s approach
contends that an organization is most concerned with the intensity of
competition within its industry. The level of this intensity is determined by
five basic competitive forces. An organization must carefully scan the task
environment to assess the importance to its success of each:
Fig
no.3.2: Porter’s Analysis
• Threat
of New Entrant
The new entrants enter
the market with new ideas and innovation. This may become threat to the new
entrants. Threat to CiBL is very high due to the following reasons given in the
next page:
o It is newly established bank
o Lower no of branches with comparison to
others
o Market share is relatively low
• Rivalry among existing firms
The competition among the
existing firms is increasing day by day. Any competitive move by one firm may
have noticeable effect on its competitors and thus may cause retaliation or
countermove. The existing banks in the industry are itself the major competitor
of the CiBL.
• Threat
of substitute products and services:
Substitute products are
those products that appear to be different but can satisfy the same need as
another product. CiBL provides the wide
range of products and services that has been able to satisfy the customers.
• Bargaining power of Buyers:
Buyers affect an industry
through their ability to force down price, bargain for higher quality or more
services. CiBL has been able to satisfy most of the need of customers by
providing the qualitative products and convenience services.
• Bargaining
Power of Suppliers:
Depositors and creditors
are considered as its actual supplier in the commercial bank because deposits
and the credits are the basic raw materials. The bargaining power of the
customers is low in the banking industries because the customers cannot bargain
over the interest rate provided on deposit. The interest rate on deposit is
comparatively higher at CiBL that is why customers prefer to keep their deposit
in this bank.
3.4
Major Competitors
In today’s economy, the
banking sector is leading sector for the economic growth and prosperity. So,
the competition in the banking sector is getting tougher. CiBL is the newly
established bank hence the existing banks of the industry are itself its
competitor. The top competitor of the industry can be shown in the following
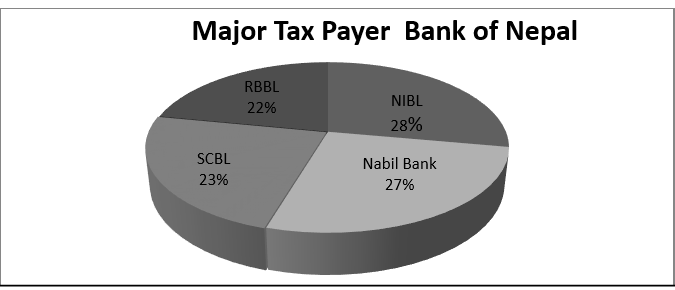
chart with respect to their tax payment as follows:
Fig
no.3.3: Major Tax Payers Bank of Nepal
The above data also
determines the competitive position of the organization within the industry.
The bank that pays the highest tax shows they are earning the higher profit.
CIBL is the newly established bank and should compete with each and every
existing bank for its market share, customers and also for the overall
profitability of the bank itself.
3.5 SWOT Analysis of CiBL
The SWOT analysis of the
CiBL can be explained with the figure as follows:
Fig
no.3.4: SWOT analysis of CiBL
CHAPTER
FOUR
ANALYSIS
OF ACTIVITES DONE AND PROBLEMS SOLVED
4.1
Analysis of Activities Performed
During the internship
period, interne have been assigned in Credit Department of the bank for two
weeks to get familiar with credit lending process, and documents required for
the credit allocation to the customers. Credit Department mainly looks after
the various documents required while processing loan makes necessary legal
documents on behalf of the bank and analyze the various risks engaged with the
loan and functioned for the mitigation of such default in the loan. In
remaining six weeks of the internship period, interne was assigned for CSD,
Marketing, and Letter of the Credit department.
4.2
Introduction to Credit Department
Credit Departments within
banks have become increasingly complex driven by the demands of regulation and
the business. The level of sophistication has accelerated in recent years as
many banks have developed credit departments with enhanced responsibilities.
The Credit Department is an independent risk oversight function. It is charged
with managing and overseeing the counterparty credit risk profile of the
Institutional Securities Business. The Credit Department’s specific
responsibilities include evaluating and rating the credit risk of counterparties,
establishing and managing counterparty credit risk limits, evaluating credit
risk transactions and approving, rejecting or modifying them as appropriate.
4.2.1
Functions of Credit Department
Some of the major
functions of the credit and loan department observed during the internship
period are as follows:
• Establishing the relationship with the
customers and informing them about the various credit instruments available as
per their requirement along with the terms and conditions.
• Analyzing the credibility of the customers
by assessing:
o Capacity of the customer for repayment of
the loan
o Collateral being put forward by customer,
whether or not, enough to meet the credit facility to be approved
o Character of the customer to recover the
loan provided
o Condition of the customer(background)
o Capital invested by the corporate
client
o Financial health of the corporation of
corporate client
o Reliable sources of individual customers to
make repayment of credit
4.3
Process of Disbursement of Loan
Banks do not provide loan
spontaneously. They undergo certain
processes in the course of granting the loan. The process of granting loan in
CiBL is as follows:
Fig
no.3.3: Process of disbursement of loan in CiBL
When the customer comes
to the Relationship manager for loan in the bank, the RM makes a proposal and
forwards it to the credit unit for approval. After the proposal is approved by
the credit unit, there is active participation of the Credit Risk Control
(CRC)/Credit Documentation Unit (CDU) for documentation, lodgment and limit
loading in the system. All the documents related to the loan are presented to
the CEO for final approval before loading the limit in the system after which
limit is loaded and the credit department releases the loan to the customers.
4.4 Types of Loan
A. Funded
In funded facilities,
there is the direct outflow of cash from the bank to the according to his/her
requirement. Bank can offer a wide variety of funded facilities depending upon
the nature of requirement.
B. Non-Funded
In non-funded facilities,
bank act as a liable holder. Bank doesn’t have to offer any cash to the client
but in the case of default by the client, the bank has to be completely liable
for the damages and cost for the third party. Thus, in the majority of non-funded
facilities, bank act as guarantor.
4.4.1
Types of Loan offered by CiBL
A. Civil Bank Personal Mortgage Loan
Basic
Eligibility Criteria:
Individuals or group of
individuals requesting for CiPML must be able to justify the following:
• The reliable and steady source of income to
serve the loan installment amount along with interest.
• Declare the purpose of the loan.
• Provide unencumbered fixed assets
collateral (land and building) fully covering the requested loan exposure.
Types of CiPML
Two types of CiPML shall
be provided depending upon the nature of the funding requirement:
• NonRevolving (CiPML I)
• Revolving (CiPML II)
Loan
Limit
• The minimum limit of CiPML is NPR. 100,000.
• The maximum limit of CiPML is NPR. 50,000,000.
Loan
Tenure
• The loan tenure of CiPML shall be fixed on
the basis of loan repayment capacity of the borrower.
• The loan tenure for CiPML (NonRevolving)
shall be fixed for the maximum of 8 years or less.
• The loan tenure for CiPML (Revolving) in
the form of overdraft shall be for maximum period of 1 year and can be renewed
on an annual basis.
Interest
Rate
The interest rate on
CiPML will be decided by the competent authority from time to time.
B. Civil Bank Home Loan
It is established as a
retail lending product to cater to the prevailing market demands.
Basic
Eligibility Criteria
Any Nepalese individual
of at least 18 years of age is eligible for Home Loan facility subject to
stable, reliable source of income. Furthermore, the disposable income should be
sufficient to serve the loan installment and due interest.
Types
of Civil Bank Home Loan Schemes
• Civil Bank Home Loan Purchase Scheme
(CiHL1)
• Civil Bank Home Loan Construction Scheme
• Civil 'Home Loan' Renovation Scheme
Loan
Limit
Civil Bank 'Home Loan'
limit shall be fixed for minimum and maximum range of NPR 100,000 and NPR
50,000,000 respectively for all types of schemes.
Loan
Tenure
The tenure of the loan
shall be for a minimum period of 5 years and the maximum period of 25 years.
This will be inclusive of the construction period and the grace period, if any.
Interest
Rate
The interest rates on the
Home Loan shall be determined by the competent authority as per the tenure of the
loan. The base rate will be the rate of interest on the Home Loan for 5 years.
The rate of interest may,
however, be revised from time to time as decided by the management.
C. Civil Bank Hire Purchase Loan
During the last decade of
banking, retail lending has established itself as one of the profitable sectors
in the banking industry. Civil Bank has therefore decided to develop and
introduce Civil Bank Hire Purchase Loan (CiHPL) as a retail lending product to
cater to the prevailing market demands. Hire Purchase Loan will be applicable
to private automobiles (cars, jeeps), commercial vehicles (trucks, buses),
heavy equipment (excavators, cranes, dozers) and other equipment (hospital
equipment, heavy kitchen equipment).
Basic
Eligibility Criteria
Any Nepalese individual
of at least 18 years of age or any company is eligible for a Civil Bank Hire
Purchase Loan facility subject to a stable, reliable source of income. The
disposable income should be sufficient to serve the loan installment and due
interest.
A company can also apply
for a CiHPL if the requirement is well justified.
Types
of CiHPL
• Civil Bank Hire Purchase Loan for Private
Vehicles (CiHPL1)
• Civil 'Hire Purchase Loan' for Commercial
Vehicles (CiHPL2)
• Civil 'Hire Purchase Loan' Heavy Equipment
Scheme (CiHPL3)
• Civil 'Hire Purchase Loan' Other
Equipment/Machines Scheme(CiHPL4)
Loan
Limit
Civil Bank 'Hire Purchase
Loan' limit will be fixed for a minimum and maximum range of NPR 500,000 and
50,000,000 respectively for all types of schemes.
Loan
Tenure
• For Scheme I and II: The tenure of the loan
shall be for a maximum period of 8 years.
• For Scheme III and IV: The tenure of the
loan shall be for a maximum period of 10 years.
Interest
Rate
The interest rates on the
Civil Bank Hire Purchase Loan will be determined by the competent authority as
per the tenure of the loan.
D. Civil Bank Loan against Fixed Deposit
Receipt
The Loan against Fixed
Deposit is an added feature in the Fixed Deposit product and enables the
depositor/accountholder to withdraw a certain percentage of the deposit amount
as a loan to cater to his/her various immediate needs.
Loan
Limit
Normally, the Bank will
finance up to 90% of the value of the FD, if the same is issued by itself. In
the case of loan against FDR issued by other Banks/financial institutions, the
Bank may not finance more than 80% of the face value. However, in exceptional
cases, the credit may be extended up to the face value of the instrument upon
approval from the competent authority. In case issuance of a performance
guarantee, the credit can be extended up to the face value of the instrument.
The rate of interest on loan against FDR should not be lower than the coupon
rate of the FD.
In case the currency of
denomination of FDR and the currency of loan is different, the Bank will not
generally finance more than 80% of the face value of the instrument. In case
the financing is more than 80%, it needs to be reviewed on the monthly basis to
guard against the foreign exchange fluctuation risk.
Loan
Tenure
The loan shall be for a
maximum tenure of 1-year renewable periodically up to the expiry date of FDR
held as security. It should be ensured that loan maturity date is prior to
Fixed Deposit Maturity date.
Interest
Rate
The interest rate on
'Loan against FDR' will be decided by the competent authority from time to
time.
E. Civil Bank Loan against Government
Bond/Securities
Loan against Government
Bond/Securities enables an individual or firm to avail a loan against the value
of the securities and bonds in their possession.
Loan Limit
Generally, Credit against
Govt. / NRB Instrument will be extended up to 90% of the value of the instrument.
However, in exceptional cases, the credit may be extended up to the face value
of the instrument upon approval from a competent authority.
Loan
Tenure
The tenure of the loan
shall be for a period of one year.
Interest
Rate
The interest rate on 'Loan
against GB' will be decided by the competent authority from time to time.
Civil Loan against Shares
(CiLS) is a product designed to cater to the various financing requirements of
various types of individual and investment firms.
Basic
Eligibility Criteria
Lending in Shares has
been highly regulated by the NRB. As such there are various requirements to be
met by the Bank as well as the Borrowers.
• A company whose share will be pledged to
the Bank must be listed in the NEPSE.
• Limits will be subjected to a maximum of
60% of the average of the last 180 days, closing price or latest closing price,
whichever is lower.
• The primary capital/net worth of the
company whose shares are proposed as security should be in the positive.
• If the proposed shares are of
banks/financial institutions, CAR of the same must be within the norms set by
NRB. Also, the auditing of the bank/financial institution should have been made
as required by the NRB directives.
• CiBL's total exposure on margin lending, including
the proposed lending, should exceed its core capital.
• Total exposure against the shares of a
specified listed company should not exceed 25% of the core capital of the Bank.
• Original share certificates should be
deposited to the Bank.
• Loan against shares should not be provided
for renewal/restructuring/rescheduling of an existing limit.
• The borrower/guarantor or their family
member should not be a director/CEO/Auditor/Secretary involved in the
management or accounting of the company whose shares have been proposed to
pledge for the loan.
• The loan limit will be assigned for a period
of one year on terminating basis. It will be nonrenewable.
• Applicant should have adequate sources of
income to service the debt and meet the margin call requirements as and when
required.
• CiLS will be revolving in nature and shall
be booked of overdraft facility in nature.
Loan
Limit
• The minimum limit of CiLS is NPR
100,000.00.
• The maximum limit of CiLS is NPR
50,000,000.
Loan
Tenure
The loan tenure for CiLS
(Revolving) in the form of an overdraft shall be for maximum period of 1 year.
This facility cannot be renewed on maturity and the loan has to be settled on
maturity. However, interest will be paid on a quarterly basis.
Interest
Rate
The interest rate on CiLS
will be decided by the competent authority from time to time.
4.5
Introduction of Credit risk
Credit risk arises
whenever a lender is exposed to loss from a borrower, obligor, or counterparty
who fails to honor their contracted debt obligation, as agreed, in a timely
manner. For lenders who extend credit in the form of loans or capital market
products, credit risk is inherent in all their business activities and is an
element in virtually every product and service that is provided.
In general, there are also degrees of
differences in the types of risks that credit transactions may hold, all of
which need to be specifically understood by the credit organization relative to
how they will impact the credit portfolio. Managing the risks that are
contained in providing debt services requires a systematic framework to be established
throughout the relevant credit areas; this is known as the credit process.
4.6
Legal Documents required for loan disbursement
• Copy of ‘Lal Purja’
• Land tax receipt
• Char Killa from ward office
• Approved map/certificate of building from
municipality or VDC
• Citizenship certificate of the owners of
the property
• Registration certificate of company(in case
the customer is a company)
• Income tax registration of company
• Copy of minimum government rate of land
4.7
Problems Solved
Credit Department is the
heart of any bank. Credit Department of any bank is responsible for the income
and profitability of the firm. The difference on the interest rate on deposits
and interest rate on loans is the income of the bank and this is called,
“interest rate spread”. After involving in the credit department of CiBL as an
intern, interne assisted the credit department head for performing different
tasks which were left pending. Internee’s assistance helped the staffs in
presenting the files and reports to the auditors quite quickly. Calculation of
various ratios of firm balance sheet and income statement takes a lot of time
for the staffs and interne helped the staff by calculating these ratios. The
followings are the major problems solved by the interne in the credit
department:
• Calculation of various ratios of B/S of
applicant’s firm
• Preparation of location maps
• Stock visit and report preparation
• Prepare checklist of documents presented by
the applicants
• Tallying the documents issued and fill up
in application form
• Operation of various machinery e.g.
photocopy, printer, fax etc
CHAPTER
FIVE
CONCLUSION
AND LESSON LEARNT
5.1
Conclusion
The internship program is
the way of implementing theoretical knowledge in real life (job place). The
internship is an academic curriculum based on practical work experience in a
particular field of study that enhances student learning. It provides great
strength for the student’s future career. Internship program not only provides
an opportunity to get exposure to the real working environment but also helps
to develop interpersonal skills and gaining knowledge on different aspects of
finance, accounting and other topics in an official setting.
Despite instability and
ongoing problems in the country, the banking sector is prospering with not many
difficulties and, therefore, gaining a major strength in the economy. CiBL,
being a new bank in the industry, is expanding its branches and services all
over the country to become the leading bank of the industry.
Interne had a great
experience working in CiBL. Especially working in Credit Department, it helps
to realize internee’s own competencies and level of understanding regarding
Banking Sector of Nepal and their proper management. This internship program
helps a lot for understanding, analyzing and interpreting about the banking
industry in Nepal as well as the function and role of the commercial bank in
our country.
5.2 Lesson Learnt
Theoretical knowledge is
vastly different than practical experiences. Working in real life situation
practically is not as simple as we think of. It requires high dedication,
commitment, and discipline. An opportunity to learn and do new things
practically in the work place at CiBL was a great experience. In fact, CiBL
helped to build knowledge horizon as to how Nepalese Financial System actually
functioned. Ability to look upon the problems carefully, skills to get
acquainted with co-workers, performing and completion of the job at the pre-determined
time, punctuality, handling of work flows effectively, coordination of activities, etc are the general things learnt
during the eight weeks of internship.
Besides, there is various
other experiences and knowledge acquisition in CiBL which are pointed out as:
• The most important lesson learnt during the
stay at CiBL was about the day to day operation of different departments and
the process involved with it
• Coordination of workforce and the various
activities for smooth operation of the bank
• Importance of time management and
punctuality
• Promotion of efficiency and effectiveness
through sincerity and confidence
• It helped to familiarize the gap between
theoretical knowledge and real life situation
• Devotion in work and sacrifices of personal
matters during office time
• Learnt to use and operate various
machinery, equipment, and systems
• Self-confidence and companionship
• Learnt to work in pressure
• Learnt to develop the interpersonal
relationship.
















EmoticonEmoticon